The Securities and Exchange Act B.E. 2535, amended version, effective on August 31, 2008 (Section 89/12), prescribed the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to lay out details and oversee connected transactions of the listed companies. Therefore, SEC issued SEC Announcement Tor.Jor.21/2551 on connected transaction rules for the listed companies to abide by.
When the listed company is doing a transaction with connected person, it may lead to the conflict of interests. To make the conduct transparent and fair to all shareholders equally, the listed company should be adhering to the following principles:
- The transaction must be approved through a transparent process by the directors and executives performing their duties with responsibility, caution, and honesty without beneficiaries involved in the decision process.
- The transaction must be for the sake of the company’s benefits, similarly to any transactions done with the third party.
- There must be a monitoring and audit system to ensure that the transaction has gone through the right process.
Definition
Connected transactions refers to transactions made by a listed company or its subsidiary with the person connected with the listed company.
Connected transactions refers to transactions made by a listed company or its subsidiary with the person connected with the listed company.
Definition |
| Connected transactions refers to transactions made by a listed company or its subsidiary with the person connected with the listed company. |
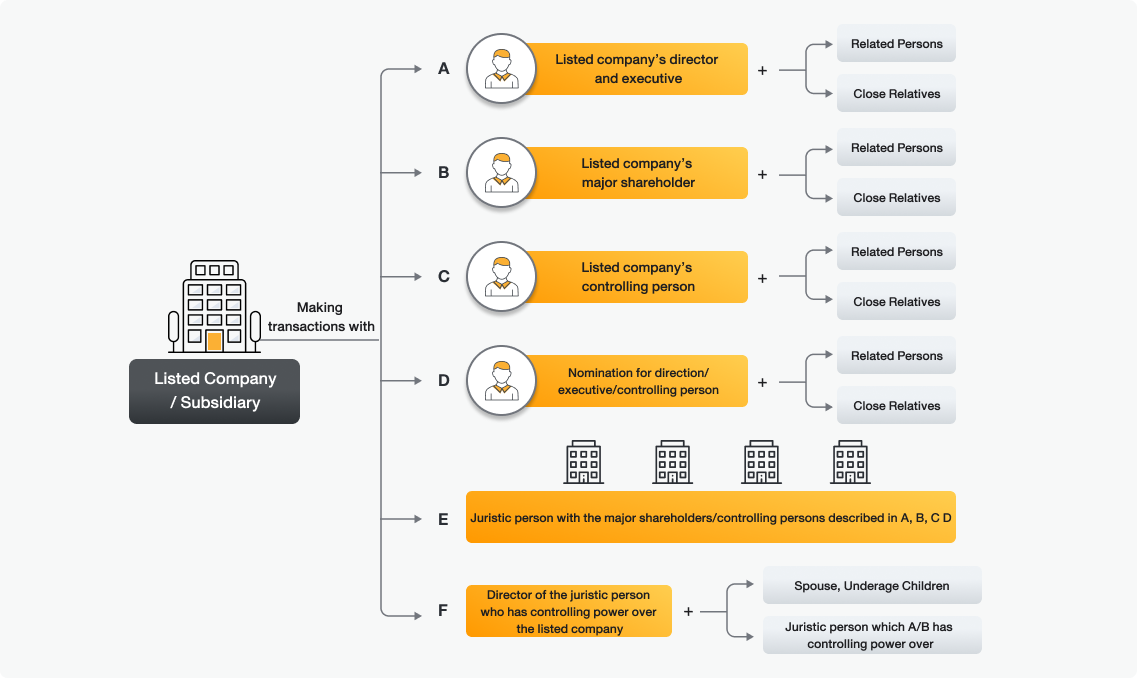
Connected person refers to a person who may have led to the conflict of interests of the company’s directors or executives, causing a conflicting situation to make a decision based on personal or corporate benefits. This includes
7.2 The company’s executive 7.3 The company’s controlling person 7.4 The director of the person with controlling power over the company 7.5 The spouse, underage offspring or adopted child of the person described in 7.1 to 7.4 |
Connected transactions refers to transactions made by a listed company or its subsidiary with the person connected with the listed company.
Connected person refers to a person who may have led to the conflict of interests of the company’s directors or executives, causing a conflicting situation to make a decision based on personal or corporate benefits. This includes
Connected person refers to a person who may have led to the conflict of interests of the company’s directors or executives, causing a conflicting situation to make a decision based on personal or corporate benefits. This includes
- The directors, executives, major shareholders, controlling person, person to be nominated for directors, executive, or controlling person position, as well as their related persons and close relatives.
- Any juristic person with major shareholders or controlling persons in (1).
- Any person whose actions can be identified as proxy or under the influence of (1) and (2).
- The director of a juristic person with controlling power.
- The spouse, underage offspring or adopted child of the director in (4).
- A juristic person under the controlling power of the person in (4) or (5).
- Any person taking action under the perception or agreement that if such action is to bring the financial benefit to the person, the following person will also gain similar benefit:
7.2 The company’s executive
7.3 The company’s controlling person
7.4 The director of the person with controlling power over the company
7.5 The spouse, underage offspring or adopted child of the person described in 7.1 to 7.4
Executive refers to the manager or the first four top-ranking executives after the manager level as well as all other 4th ranking equivalent, and accounting or finance executives of department head level and up.

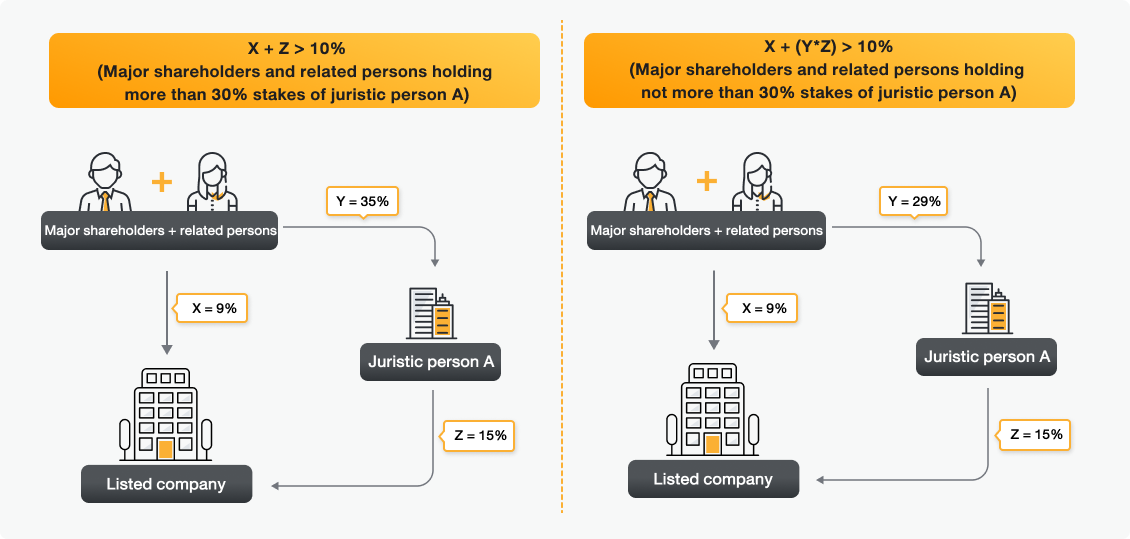
Major shareholder refers to a direct and indirect shareholder of a juristic person with more than 10% holding of voting shares of the juristic person. This includes the holding of related person as follows
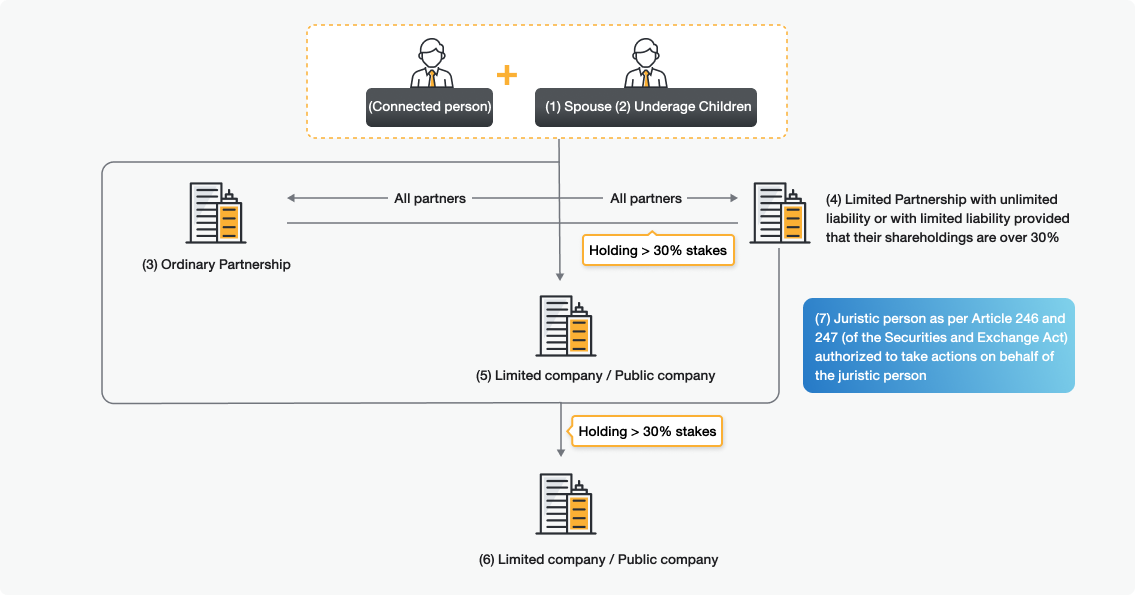
Related person refers to the person relating to the connected person, which means the person or the Ordinary Partnership described as per Article 258 (1)-(7) of the old Securities and Exchange Act B.E. 2535 as follows
- Spouse
- Underage children
- Ordinary Partnership where the person as well as (1) or (2) are partners
- Limited Partnership where the person as well as (1) or (2) are partners with unlimited liability or with limited liability provided that their holdings are over 30%
- Limited company or public company where the person plus (1) or (2) or (3) or (4) collectively hold more than 30% stakes
- Limited company or public company where the person plus (1) or (2) or (3) or (4) or (5) collectively hold more than 30% stakes
- Juristic person as per Article 246 and 247 (pursuant to the prior version of the Securities and Exchange Act) authorized to take actions on behalf of the juristic person
Controlling persons refer to the person with the controlling power over the company, which means
- Holding the voting shares of a juristic person more than 50% of the company’s total voting shares
- Having control over majority votes at the juristic person’s shareholder meeting, either directly or indirectly or by any reason
- Controlling an appointment or discharge of more than half of the directors, either directly or indirectly
Close relatives refer to the person having blood relations or legal relations by registration, who are
- Spouse
- Father
- Mother
- Siblings
- Offspring and spouse of the offspring
Type of the connected transactions |
The connected transactions can be categorized into 5 types
| Type | Description | Examples |
| 1. Ordinary business transactions | Commercial transactions that a listed company or its subsidiary normally makes to operate business under general commercial conditions | Selling goods, buying the raw materials, and providing services |
| 2. Ordinary business support transactions | Transactions made to support ordinary business under general commercial conditions | A hire for goods shipment, advertisement production, management contract, and receiving technical assistance |
| 3. Real estate rental transactions for a period not longer than 3-year span | Rental transactions with no more than 3-year contract period, and without proof of general commercial conditions | Renting a building as office, or renting a building or land for warehousing |
| 4. Transactions relating to assets or services | Transactions about the acquisition or disposition of assets, or the right to get or receive the service | Buying the machine, buying investment capital, selling a building, selling the land leasehold or concession |
| 5. Providing or receiving financial assistance | Providing financial assistance | Offering the loans or guarantee |
| Receiving financial assistance | Borrowing loans, paying fees for the connect persons’ credit line used by the company, paying fees to connected persons regarding the loan guarantee |
Calculation of the transaction size and how to handle it |
- Value used for the calculation of the transaction size
| Transactions | Value used for the calculation of the transaction size | Examples |
| 1. Asset or service | Highest of transaction value, book value, or market value | The sale of land at agreed upon value of 200 million Baht, when its book value was at 150 million and the appraisal value by independent appraiser was 198 million Baht, the value to be used to calculate the transaction size would be 200 million Baht. |
| 2. Providing financial assistance | The principal and interested throughout the loan period, or the guarantee value in line with potential damages when the connected person becomes default | In case of 20 milion Baht loan for a period of two years, at 5% interest, the value to be used to calculate the transaction size would be 22 million Baht as per this formula (20+(20x5%x2)). |
| 3. Receiving financial assistance | The reward or benefit to be paid to connected persons through the period of the financial assistance. | In case of 20 milion Baht loan for a period of two years, at 5% interest rate, the value to be used to calculate the transaction size would be 2 million Baht as per this formula (20x5%x2). |
| 4. Disposition of capital investment to the extent that the subsidiary or affiliate no longer exists | Total rewards to be gained including borrowed money (principal plus interest), the guarantee, or other liabilities that the listed company or its subsidiary has to be responsible for. | In case the company has sold all of its investment in the subsidiary to the major shareholder at 100 million Baht, when the subsidiary has 50 million Baht liability (loan plus interest) accrued to the listed company, the value to be used to calculate the transaction size would be 150 million Baht |
- Multiple connected transactions can be included into one if the transactions have been intentionally separated to avoid the rules. An inclusion should be for all other transactions made six months prior to an agreement to do the transaction by the same person, his/her related person or close relatives. Nevertheless, this would not include the connected transactions approved by the shareholders.
- The company should measure the size of transaction to prepare for the case of any possible connected transactions and how to handle them. The company should compare the transaction value against the higher one between the two references as per the latest financial statement (X is the transaction value)
| Transaction size | Choose the maximum value between | |
| Small | X ≤ 1 million Baht | X ≤ 0.03%NTA* |
| Medium | 1 million Baht < X < 20 million Baht | 0.03%NTA* < X < 3%NTA* |
| Large | X ≥ 20 million Baht | X ≥ 3%NTA* |
* Net total assets (NTA) refers to Total assets – intangible assets – total liability – non-controlling interests (if any) (Intangible assets are, for example, the goodwill and deferred charges. Exceptions are for intangible assets that generate major income such as the concession and patent permit.)
In case of consolidated financial statements, NTA value from the consolidated financial statements will be used
In case of consolidated financial statements, NTA value from the consolidated financial statements will be used
- Size of each type of transactions and how to process
| Type of transaction | Authority | ||
| Small | Medium | Large | |
| 1. Normal business transactions/ 2. Normal business-support transactions - General commercial conditions | The company’s board of directors approve in principal and lay down the framework for the management to proceed | ||
| - No general commercial conditions | The Management | Board of directors + Information disclosure to SET | Shareholders |
| 3. Rental or rented real estate for not longer than 3-year period, and under no general commercial conditions | The Management | The Management + Information disclosure to SET | Board of directors + Information disclosure to SET |
| 4. Transactions relating to products or services | The Management | Board of directors + Information disclosure to SET | Shareholders |
| 5. Transactions on offering or receiving financial assistance | |||
| 5.1 Providing financial assistance to a related party as follows; * a related party who is an individual * a related party that is a juristic person, which a listed company or its subsidiary, holding shares in a lower proportion than other related parties who are not listed companies or subsidiaries, as the case may be, in that juristic person | - | Board of directors + Information disclosure to SET (<100 million Baht or <3%NTA, whichever is lower) | Shareholders (≥ 100 million Baht or ≥3%NTA, whichever is lower) ✪ |
| 5.2 Transactions involving the provision or receipt of financial assistance other than those specified in 5.1 | The Management | Board of directors + Information disclosure to SET | Shareholders ✪ |
Remark
✪ In cases where a listed company or its subsidiary, together with related parties, jointly provide financial assistance to a juristic person in which the listed company, its subsidiary, and related parties hold shares in proportion to their respective equity interests, and such assistance is granted under general commercial terms or better, the listed company shall be exempted from obtaining shareholder approval for such transaction.
General commercial conditions refer to the commercial transactions under fair pricing and conditions, which do not lead to the benefit transfer. This includes
✪ In cases where a listed company or its subsidiary, together with related parties, jointly provide financial assistance to a juristic person in which the listed company, its subsidiary, and related parties hold shares in proportion to their respective equity interests, and such assistance is granted under general commercial terms or better, the listed company shall be exempted from obtaining shareholder approval for such transaction.
General commercial conditions refer to the commercial transactions under fair pricing and conditions, which do not lead to the benefit transfer. This includes
- The prices and conditions which the listed company or its subsidiary gain or offer to general people
- The price and conditions which connected person offer to general people
- The price and conditions which the listed company can prove that similar business operators have offered to general people as well.
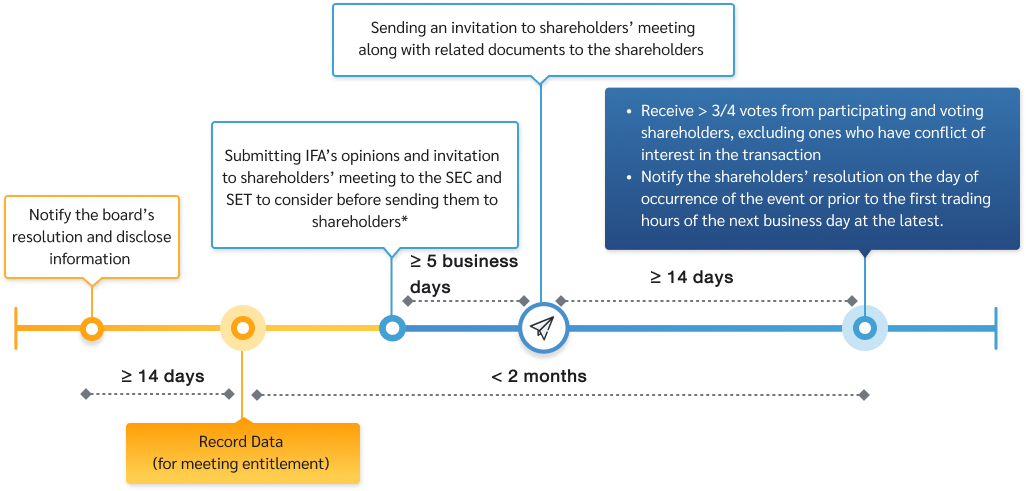
Gaining an approval the shareholder meeting must be at least three-quarter of participating and voting shareholders, excluding interested shareholders. In doing so, IFA (independent finance advisor) must be appointed and express views regarding the transactions including the rationality and benefits to the company, fairness of prices and conditions, as well as risks
In case the connected person is a state agency, juristic person established by specific law, or the business owned by state agency or by juristic person stabled by specific law, the company will not be required to gain approval from the shareholder meeting once the board of directors have already approved.
Transactions exempted from the connected transaction rules |
| Loan offering as per the employee welfare rule |
| Transactions of which the counterparty of listed company, or both parties are A subsidiary in which the listed company hold no less than 90% stakes A subsidiary in which the director, executives, or related persons hold shares or has the interest in, directly or indirectly, no more than the rate determined by the Capital Market Supervisory Board, or has the required qualifications. |
| The listed company has made the transactions with its subsidiary, in which the connected persons holds no more than 10% stakes and has no controlling power over the subsidiary. |

| Connected transactions between the listed company’s subsidiaries, in which the connected persons hold no more than 10% stakes and are not the controlling person over the subsidiaries. |

The listed company or its subsidiaries has issued new securities to connected persons in the following manners
|
| The transactions which were made by the listed company or subsidiary with a juristic person, in which the listed company or subsidiary has sent someone to take control. |

| The transactions proven to be fair and did not lead to the benefit transfer. |
Information disclosure |
- The company has to notify, via SETLink, about the board resolutions on the connected transactions immediately upon making the transaction (normally on the day the board has given an approval), that is within the day the board has made the resolution or prior to the first trading hours of the next business day at the latest.
- Key information of the board resolution are
- Date, month, year of the transaction and the name of counterparty
- Description about the assets, services, financial assistance to be provided or received, and in case of investment capital, the name and type of business must be specified as well as the business operations, summary of the financial statements and operational performance, list of major shareholders, and the directors.
- Total value and the measurement of total value, total transaction value, payment method, conditions, interest rate, interest payment terms, and the guarantee (if any)
- Names of the connected persons and how they are connected.
- Description and scope of the connected persons’ stake in making connected transactions.
- The source of fund for buying assets, and financial assistance and the fund adequacy. In case of loan, possible conditions that may affect the shareholder rights must be specified such as the limitation to pay dividend.
- Specify the names of directors having the interest and/or directors who are connected persons, and specify that the mentioned persons had not attended the director meeting and had no voting right.
- The views of the board of directors about an agreement to enter into the transaction in terms of the rationality, the company’s optimum benefit compering a transaction with an outside independent person, as well as associated risks.
- The opinion of an audit committee and/or the directors that differ from the board of directors.
Comments of independent financial advisor (IFA) |
- IFA has to express his/her views regarding the transaction to the board to directors on
- The rationality and benefits to the listed company
- Fairness of the price and conditions
- Reasoning about whether the shareholders should vote for an approval of the transaction
- The company must send the IFA’s comments along with an invitation to shareholder meeting to the SEC and SET to consider about an adequacy of information. The submission can be in either one of these two ways
- Sending the documents at least 5 business days before sending them to the shareholders
- Sending the documents at the same time as with the shareholders
Sending an invitation to shareholder meeting to the shareholders |
- Submitting period An invitation letters must be sent to shareholders at least 14 days ahead of the meeting date
- Information to be included in the invitation are the IFA’s opinions and the following documents
- Information disclosed to SET once the company agrees to enter into the transaction
- Summary of company information e.g. list of executives and major shareholders, business operations and trends, inter-company transactions, 3-year financial summaries and latest financial statement with MD&A , risk factors, and financial forecasts (if any).
- Names and number of shares held by shareholders who has no voting right
- Opinions of independent experts such as the asset appraiser
- The company must nominate at least one audit committee member to be a proxy of the shareholders
- Views of the board of directors regarding the rationality and optimum benefits toward the company comparing to making a transaction with an outside party.
Process of getting approval on connected transactions from the shareholders’ meeting
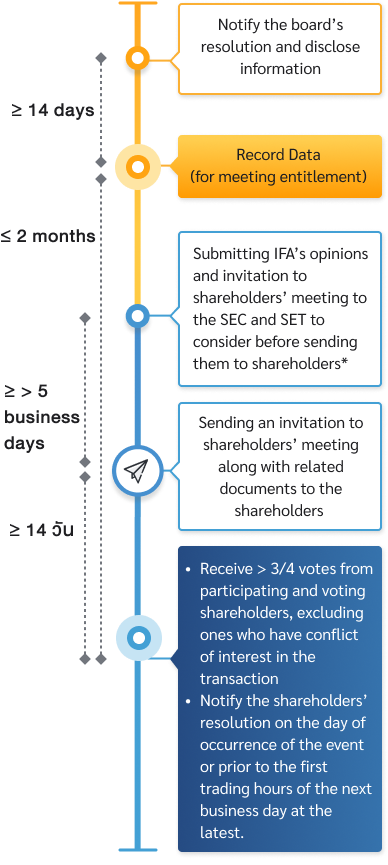
* SP sign is posted 3 days prior to the book closing date until the capital reduction is completed. Also, SET has been informed and provided with complete documents
Related Regulations
|
|
|
| Type of information | Download | Timing of disclosure * |
| 1. Connected transactions |  | Immediately |
* Immediately: information to be disclosed by 9 a.m. on the next working day or on the event date (The date of the board of directors or shareholders meeting's have resolution) 3 working days: Information to be disclosed within 3 working days after the event date


